What is Graphene and What is Graphene Used For?
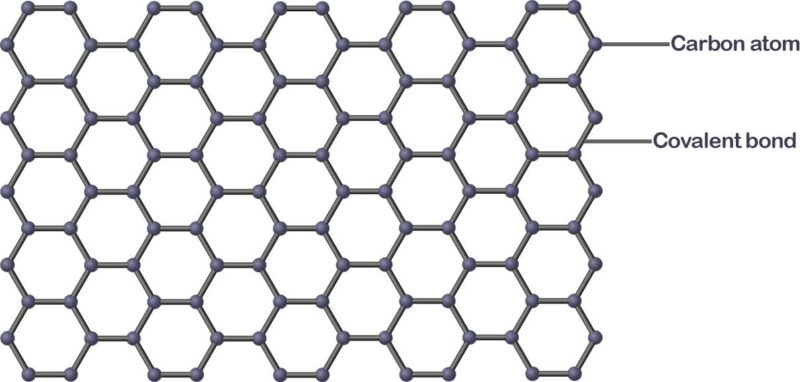
What is Graphene and what is Graphene used for in our daily lives? Graphene is made of a single sheet of carbon atoms arranged in a crystal lattice (like a honeycomb pattern). It is the basic building block of graphite, the material that is used in pencil lead.
Graphene is probably a word that you’ve never heard of. But it’s actually a powerful material on Earth. It even is making rounds in the field of science and technology. Get to know what graphene is all about and what it is made of.
When being isolated from graphite, graphene is one atom thick and is two-dimensional. It is made up of wondrous properties that no substance can ever pass that. As such, it is hailed by many as a supermaterial.
Graphene is technically composed of carbon atom and a covalent bond that formed a honeycomb pattern.
How strong is graphene?
Graphene was discovered about 14 years ago, and it has been tagged the world’s strongest material as it is over 200 times stronger than steel – that’s a daredevil level of rigidity. Also, Graphene is obviously stronger than Diamond. The rigidity of Graphene has been tested over and again by different researchers, and it has been confirmed that Graphene is indeed a formidable raw material with lots of unique properties.
The structure of Graphene is all about carbon atoms bonding with each other all through; however, each carbon in the structure is also connected to three other carbon atoms, and that’s how the bond remains strong and robust.
Nevertheless, irrespective of the rigidity of Graphene, it is yet porous, lightweight, and flexible. Because Graphene is strong, lightweight and flexible, various industries are exploiting Graphene as raw material to revolutionize their products – adding more strength, antiviral properties, and more revolutionary features.
Nevertheless, as strong as Graphene is, it has a melting point – if stretched to a certain length, it could break.
What is the melting point of graphene
As researches keep going on to discover the full capabilities and features of the world’s wonder raw material – Graphene, it is important that you know the predicted melting points of graphene. Some researchers have assumed that graphene’s melting point is about Tm ≈ 4900 K. However, graphene and its referents (graphene oxide) predictably show high melting points than many other materials.
A hypothetical-based test showed results of a freestanding graphene melting at Tm 4510K. But, the test did not take into consideration the multifarious bonding patterns in the melting process. Further researches to proof this theoretical result have been a challenging one for researchers over the years.
Nevertheless, it is vital to understand the melting point of graphene in order to know how to use the material in designing/constructing other products. A team of physicists from the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology and Institute for High-Pressure Physics of the Russian Academy of Sciences have declared that the melting of graphene is sublimation.
However, a post from the Royal Society of Chemistry, satisfies that graphene has a melting point between 4000 to 6000 Kelvins.
What is the hardness of graphene
Graphene may have proved to be the strongest material ever known to man, but is it the hardest? A quick answer to that question is – NO! Graphene isn’t the hardest material out there. The tensile strength of graphene is about 130GPa, 1 TPI, which is about 150000000psi. This is quite impressive to say, but Diamond has continuously proved that it is harder than graphene.
Graphene is surprisingly soft, lightweight, and arguably sublimates as its form of melting. The soft nature of graphene can be explained in this manner – when you scribe a 4B pencil; you can see that the graphite used is utterly soft. Well, this is because the carbon layers tend to shave off very easily; however, the atoms in those layers bond to each other severely. Thus, while graphene is strong, it is not hard.
The chemical properties of graphene made it the strongest material we have at the moment, but Diamond has Young’s modulus of 250GPa – that’s far ahead of graphene.
Graphene Applications
With the amazing properties and characteristics that make up the graphene, it is highly applicable in various fields. And interestingly, graphene is the key to improve and revolutionize these key industries:
Energy
Graphene has the potential to keep energy. Due to its amazing electrical and thermal conductivity, graphene can be used as super batteries, supercapacitors, and wind and solar panels.
Thanks to graphene, the lifespan of a traditional lithium-ion battery will dramatically increase. Thus, charging your electronic devices quickly and keeping your battery last for days even after extreme usage.
Coatings
With the high resistivity of graphene, the development of durable coatings is realized. And by durable, that means the coatings are hydrophobic, conductive, and chemically-resistant. Even better, they are resistant to cracks. For some coatings, they can even be resistant to scratches and UVA exposure. Thus, making it a huge market potential.
Sensors
Graphene is a key material to use for ultra-sensitive sensors. With graphene-based sensors, harmful minuscule particles can be detected easily thanks to the atoms in graphene that can sense changes in surroundings easily. Moreover, it has even paved the way for the creation of micrometer-sized sensors, with the capability of detecting substances at a molecular level.
Besides the detection of harmful substances, graphene also helps in monitoring vital crops in agriculture. Graphene-powered sensors will help farmers monitor harmful gasses that are causing an impact on crop fields so they can take action fast. Additionally, graphene sensors can monitor the atmospheric conditions of areas to know which one is ideal for certain crops to grow.
The future is bright and bold for graphene, and it’s making a way to bring a better impact on the world. We may be at graphene’s infancy stage. But towards the upcoming years, scientists and researchers around the world will see the potential that graphene brings to every industry.
What Are The Characteristics of Graphene?
As pointed out, graphene has wondrous properties. Here are some of the major characteristics that make up this supermaterial.
1. Hardness
Graphene is the world’s strongest material. It has a strength of 42 N/m, which has an intrinsic strength of 130 GPa (gigapascals). It is even 200x stronger than the strongest steel.
2. Elasticity
Graphene is also highly elastic. No matter how strained it is, graphene is still able to maintain its initial size. Based on the Atomic Force Microscopic (AFM) tests carried on graphene sheets, it showed that graphene sheets had spring constants in the region of 1-5 N/m and Young’s modulus of 0.5TPa.
3. Lightweight
Despite being the toughest material, graphene is also lightweight. In fact, it weighs 0.77 milligrams per square meter. It is said that a single sheet of graphene would weigh under 1 single gram.
4. Good electrical conductor
With the low defect density of the crystal lattice, graphene has the highest electrical conductivity.
5. Transparent
Graphene can only absorb about 2.3% of reflecting light, despite being an atom thick. It is even better than ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) nanoparticles, which is commonly used to fabricate transparent conductive films.